What Is Vitamin B Complex Good For?
B Vitamins are necessary for a healthy life. Each vitamin plays an important role in development and maintenance of the brain and nervous system, as well as other organs and systems. And all of them work together in the body to convert food into energy. Because their functions are interrelated, a deficiency or insufficiency in one may negatively affect the function of another.
There are eight B Vitamins:
One of them, Vitamin B2, is in my list of top tier nootropics. Another, Vitamin B3, is in my list of top tier geroprotectors. Various substances have been or are sometimes associated with the B4, B8, B10, and B11 classifications. However, consensus science does not currently recognize them as vitamins.
Most B Vitamins have multiple vitamers. Vitamins are functional classifications, and vitamers are the molecular structures within each classification. Vitamers of a particular vitamin may differ in effects beyond the functions essential to the vitamin. Some differences may be complementary, and some may present different opportunity and risk profiles.
Because the body cannot synthesize them, B Vitamins must come from a balanced diet. Deficiency is associated with adverse effects ranging from a weakened immune system to heart disease. According to a 2011 study on nutrient sources in the United States, between 2% and 12% of people consume less than the estimated average requirements (EAR) of B Vitamins from natural and fortified food sources.

Regulatory agencies have established guidance to help consumers avoid adverse effects associated with vitamin deficiencies. Guidance includes recommended daily allowances and adequate intakes (RDI) in the United States. And the European Union provides nutrient reference values (NRV), which are a subset of dietary reference values (DRV) that apply to vitamins.
Larger but unknown percentages of people consume less than optimal amounts of B Vitamins. This insufficiency is also associated with adverse effects, as described by a 2012 report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention:
“Dietary deficiencies are well documented, and they have characteristic signs and symptoms. In addition, recent findings have determined that less than optimal biochemical concentrations (representing suboptimal status) have been associated with risks of adverse health effects. These health effects include cardiovascular disease, stroke, impaired cognitive function, cancer, eye diseases, poor bone health, and other conditions.”
Optimal intake of B Vitamins may vary significantly from person to person. Because all B Vitamins are water-soluble, excess amounts are usually eliminated from the body. So they are generally safe to consume at higher amounts than those specified by RDI or NRV.
However, caution is still warranted. Regulatory agencies have established guidance on the upper limit (UL) of daily intake likely to pose no risk of adverse side effects. And it’s always wise to seek medical advice from your physician before and during use of all dietary supplements.
Vitamin B Complex
Vitamin B Complex is the combination of all eight B Vitamins in a single supplement. Taking B Complex at safe high doses may be an effective strategy for optimizing intake with little risk. Safe high doses are those above RDI and below UL.
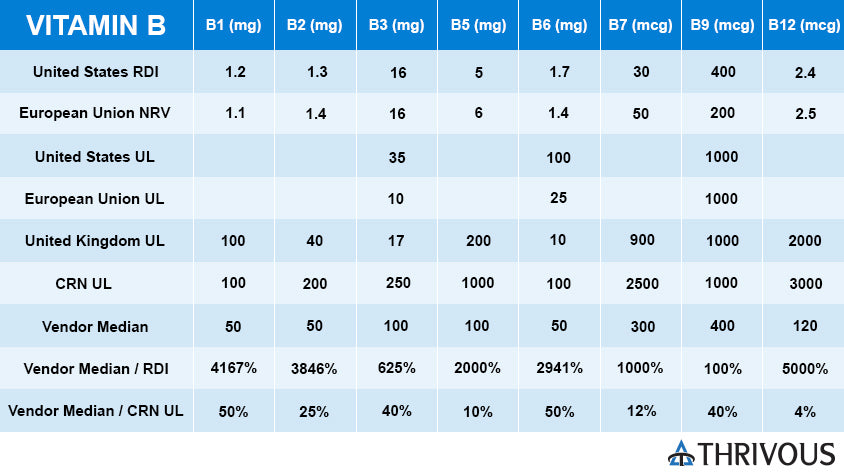
Most vendors that sell Vitamin B Complex follow a safe high dose strategy. Consider the top B Complex products for sale on Amazon.com. Among them, the mean dose for all B Vitamins except B9 is well above RDI. And none of the mean doses is above UL as set by the Council for Responsible Nutrition (CRN).
Supplementation of high dose B Complex may support brain health and improve mental performance, according to these studies:
- B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy – A Review. In 2016, this review concluded that "administration of the entire B-vitamin group, rather than a small sub-set, at doses greatly in excess of the current governmental recommendations, would be a rational approach for preserving brain health."
- Functional Brain Activity Changes after 4 Weeks Supplementation with a Multi-Vitamin/Mineral Combination: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial Exploring Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Steady-State Visual Evoked Potentials during Working Memory. In 2016, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study of supplementation including high-dose Vitamin B Complex found "preliminary evidence of changes in functional brain activity during working memory associated with 4 weeks of daily treatment with a multi-vitamin and -mineral combination in healthy adults".
- Multivitamins and minerals modulate whole-body energy metabolism and cerebral blood-flow during cognitive task performance: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. In 2016, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study of supplementation including Vitamin B Complex found that “brain function and metabolism are amenable to micronutrient supplementation, even in adults who are assumed to have nutritional status typical of the population”.
- Effects of Four-Week Supplementation with a Multi-Vitamin/Mineral Preparation on Mood and Blood Biomarkers in Young Adults: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. In 2015, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study of supplementation including high-dose Vitamin B Complex found that “supplementation may have beneficial effects on mood, underpinned by elevated B-vitamins and lowered homocysteine in healthy young adults”.
- Acute mood but not cognitive improvements following administration of a single multivitamin and mineral supplement in healthy women aged 50 and above: a randomised controlled trial. In 2015, this placebo-controlled study of supplementation including high-dose Vitamin B Complex found that supplementation “reduces stress several hours after intake in healthy older people”.
- Effects of multivitamin, mineral and herbal supplement on cognition in younger adults and the contribution of B group vitamins. In 2014, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study of supplements including high-dose Vitamin B Complex found that 'supplementation may be useful for maintaining levels of B vitamins." And "the effects of multivitamins on speeded attention such as the stroop task in young [male] adults warrant further investigation."
- Effects of vitamin and mineral supplementation on stress, mild psychiatric symptoms, and mood in nonclinical samples: a meta-analysis. In 2013, this meta-analysis of eight studies found that "micronutrient supplementation has a beneficial effect on perceived stress, mild psychiatric symptoms, and aspects of everyday mood in apparently healthy individuals." And "supplements containing high doses of B vitamins may be more effective in improving mood states."
- The effects of multivitamin supplementation on diurnal cortisol secretion and perceived stress. In 2013, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study observed that an "elevation in [Cortisol Awakening Response] associated with multivitamin supplementation [including high dose B Complex] … represents an adaptive response to everyday demands in healthy participants."
- The effects of multivitamin supplementation on mood and general well-being in healthy young adults. A laboratory and at-home mobile phone assessment. In 2013, this study found “significantly reduced stress, physical fatigue and anxiety in the [multivitamin including high dose B Complex] group in comparison to placebo across a number of time points”.
- Participant experiences from chronic administration of a multivitamin versus placebo on subjective health and wellbeing: a double-blind qualitative analysis of a randomised controlled trial. In 2012, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found “a range of subjective beneficial effects that are consistent with quantitative data from previously published randomised controlled trials examining the effects of multivitamins and [high dose] B vitamin complexes on mood and well-being”.
- Effects of a multivitamin, mineral and herbal supplement on cognition and blood biomarkers in older men: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. In 2012, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that "relatively short-term supplementation with a multivitamin [including high dose B Complex] can benefit these risk factors for cognitive decline." And "daily multivitamin supplementation may improve episodic memory in older men at risk of cognitive decline."
- Memory improvements in elderly women following 16 weeks treatment with a combined multivitamin, mineral and herbal supplement: A randomized controlled trial. In 2012, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that “Sixteen weeks supplementation with a combined multivitamin, mineral and herbal formula [including high dose B Complex] may benefit working memory in elderly women at risk of cognitive decline”.
- Neurocognitive effects of multivitamin supplementation on the steady state visually evoked potential (SSVEP) measure of brain activity in elderly women. In 2012, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that “in the elderly, multivitamin supplementation [including high dose B Complex] may enhance neural efficiency during memory retrieval”.
- The effects of multivitamins on cognitive performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. In 2012, this meta-analysis found that “multivitamins were found to enhance immediate free recall memory but no other cognitive domains”.
- Vitamins and cognition: what is the evidence? In 2011, this analysis found that “whereas studies involving supplementation with single vitamins, or restricted ranges of vitamins, have demonstrated equivocal results, evidence from studies involving the administration of broader ranges of vitamins, or multivitamins, suggest potential efficacy in terms of cognitive and psychological functioning”.
- The effect of 90 day administration of a high dose vitamin B-complex on work stress. In 2011, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that “[high dose] vitamin B complex treatment groups reported significantly lower personal strain and a reduction in confusion and depressed/dejected mood after 12 weeks”.
- Vitamins and psychological functioning: a mobile phone assessment of the effects of a B vitamin complex, vitamin C and minerals on cognitive performance and subjective mood and energy. In 2011, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that "participants in the vitamin/mineral group rated themselves as having greater 'physical stamina' … greater 'concentration' and 'mental stamina' … [and] greater subjective 'alertness.'" It concluded that "healthy members of the general population may benefit from augmented levels of vitamins/minerals via direct dietary supplementation."
- The effect of multivitamin supplementation on mood and stress in healthy older men. In 2011, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that a supplement with high dose B Complex "may be useful in improving alertness and reducing negative mood symptoms." And it "may also improve feelings of general day-to-day well-being."
- Effects of high-dose B vitamin complex with vitamin C and minerals on subjective mood and performance in healthy males. In 2010, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that "healthy members of the general population may benefit from augmented levels of vitamins/minerals [including high dose B Complex] via direct dietary supplementation." And "supplementation led to improved ratings of stress, mental health and vigour and improved cognitive performance during intense mental processing."
- Effects of a multi-vitamin/mineral supplement on cognitive function and fatigue during extended multi-tasking. In 2010, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that "the vitamin/mineral [including B Complex] group exhibited an attenuation of the negative effects of extended task completion on mood/fatigue." And the "multi-tasking performance for this group was also improved in terms of accuracy across all tasks." It concluded that "healthy members of the general population may benefit from augmented levels of vitamins/minerals via direct dietary supplementation."
- Cognitive and mood effects in healthy children during 12 weeks' supplementation with multi-vitamin/minerals. In 2008, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that “vitamin/mineral supplementation [including low dose B Complex] has the potential to improve brain function in healthy children”.
- Effect of B vitamins-fortified foods on primary school children in Beijing. In 2006, this study found that "The effect of B vitamin compound supplementation is better than that of single riboflavin supplementation ... [and] micronutrient supplementation appears to assist children's study abilities".
These studies had divergent results:
- Improved Blood Biomarkers but No Cognitive Effects from 16 Weeks of Multivitamin Supplementation in Healthy Older Adults. In 2015, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that “in healthy older people, multivitamin supplementation [including high dose B Complex] improved a number of blood biomarkers that are relevant to cognition, but these biomarker changes were not accompanied by improved cognitive function”.
- Long-term multivitamin supplementation and cognitive function in men: a randomized trial. In 2013, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that “in male physicians aged 65 years or older, long-term use of a daily multivitamin [including low dose B Complex] did not provide cognitive benefits”. This study commented regarding itself that “doses of vitamins may be too low or the population may be too well-nourished to benefit from a multivitamin”.
- B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy – A Review. In 2016, this review commented on weaknesses in the 2013 study. It criticized "a relatively crude cognitive assessment undertaken over the telephone." And it observed that "there was no evidence of declining performance over the 12 years of the study in either the placebo or multivitamin groups."
- The Case is Closed: Editorial Bias Prevents Reasonable Evaluation of Dietary Supplements. In 2014, this review commented on the 2013 study. It observed that subjects "were only prevented from taking other multivitamins if those products contained more than the US RDA of vitamin E, vitamin C, β-carotene, or vitamin A." And "this means they could have consumed high levels of B vitamins."
- Effect of multivitamin and multimineral supplementation on cognitive function in men and women aged 65 years and over: a randomised controlled trial. In 2007, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found "no evidence for a beneficial effect of daily multivitamin and multimineral supplements [including low dose B Complex] on these domains of cognitive function." However, it observed that "the possibility of beneficial effects in older people and those at greater risk of nutritional deficiency deserves further attention."
- Cognitive performance in relation to vitamin status in healthy elderly German women-the effect of 6-month multivitamin supplementation. In 2005, this study found that “6 months supplementation of physiological dosages of antioxidants and B vitamins have no effect on cognitive performance in presumedly healthy and well-nourished female seniors”.
Supplementation of subsets of B Vitamins may NOT support brain health and improve mental performance, according to these meta-analyses:
- Effects of homocysteine lowering with B vitamins on cognitive aging: meta-analysis of 11 trials with cognitive data on 22,000 individuals. In 2014, this meta-analysis found that “homocysteine lowering by using [B9 alone or in combination with B12] vitamins had no significant effect on individual cognitive domains or global cognitive function or on cognitive aging”.
- B-vitamin trials meta-analysis: less than meets the eye. In 2015, this review commented regarding the 2014 meta-analysis that “although the sheer volume of data incorporated into this analysis testifies to the industriousness of its authors, few other conclusions can be drawn”.
- Homocysteine lowering, B vitamins, and cognitive aging. In 2015, this review commented regarding the 2014 meta-analysis that “we are concerned about 3 aspects of this analysis: the choice of trials, the cognitive assessment tools, and the analysis and interpretation of data”.
- Assessing the association between homocysteine and cognition: reflections on Bradford Hill, meta-analyses, and causality. In 2015, this review commented on the 2014 meta-analysis. It claimed that "no conclusion can be made regarding the effects of homocysteine-lowering on cognitive decline, since the trials typically did not include individuals who were experiencing such decline."
- Effect of Homocysteine Lowering Treatment on Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. In 2012, this meta-analysis found that “supplementation of vitamins B12, B6, and folic acid alone or in combination does not appear to improve cognitive function in individuals with or without existing cognitive impairment”.
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2012 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
- B-vitamins and fatty acids in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease and dementia: a systematic review. In 2010, this meta-analysis found “insufficient evidence to draw definitive conclusion on the effect of B vitamins [B9 alone or in combination with other B Vitamins] and fatty acids for the treatment of cognitive decline, dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease”.
- Effect of folic acid, with or without other B vitamins, on cognitive decline: meta-analysis of randomized trials. In 2010, this meta-analysis found “no effect of folic acid, with or without other B vitamins, on cognitive function within 3 years of the start of treatment”.
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2010 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
- Folic acid with or without vitamin B12 for the prevention and treatment of healthy elderly and demented people. In 2008, this meta-analysis found that “the small number of studies which have been done provide no consistent evidence either way that folic acid, with or without vitamin B12, has a beneficial effect on cognitive function of unselected healthy or cognitively impaired older people”.
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2008 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
- Vitamin B6, B12, and folic acid supplementation and cognitive function: a systematic review of randomized trials. In 2007, this meta-analysis reviewed studies on combinations of B6, B9, and B12. It found that they do "not yet provide adequate evidence of an effect … on cognitive function testing in people with either normal or impaired cognitive function."
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2007 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
This meta-analysis had divergent results:
- Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials of folate and vitamin B12 for depression. In 2015, this meta-analysis found that “treatment with folate and vitamin B12 does not decrease the severity of depressive symptoms over a short period of time, but may be helpful in the long-term management of special populations”.
Vitamin B1
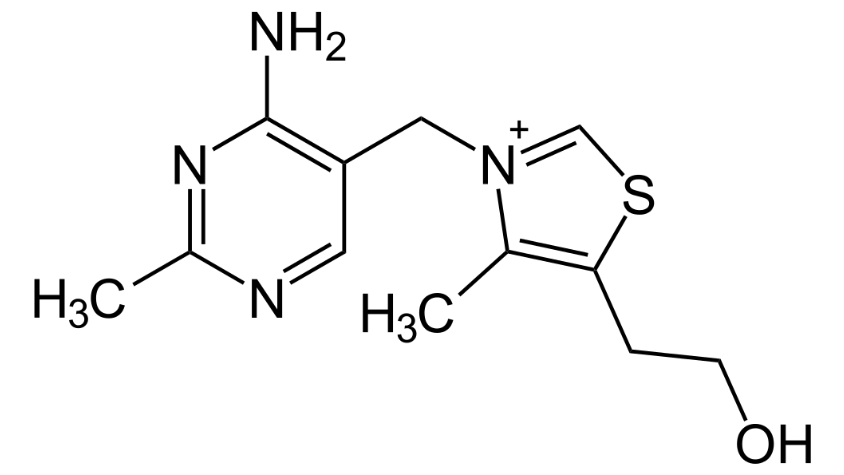
Vitamin B1 vitamers include Thiamin (Thiamine or Aneurin) and Thiamine Pyrophosphate (Thiamine Diphosphate or Cocarboxylase). They are found in foods like enriched, fortified, or whole-grain products; bread and bread products, mixed foods whose main ingredient is grain, and ready-to-eat cereals.
Regulatory agencies recommend that you consume between 1.1 mg and 1.2 mg daily. In the United States, recommended daily intake (RDI) is 1.2 mg. In the European Union, the nutrient reference value (NRV) is 1.1 mg.
Supplements are generally safe up to at least 100 mg daily. In the United States and the European Union, UL is not determined. In the United Kingdom, UL is 100 mg. CRN also sets its UL at 100 mg.
The maximum absorption per dose is above the CRN UL. The bioavailability of Thiamin and Thiamin Pyrophosphate may be roughly equivalent. And disulfides (such as Allithiamine and Sulbutiamine) may provide greater neuroavailability than alternatives.
Supplementation may decrease risk of dietary deficiency and insufficiency. In the United States, EAR is 1 mg. Before supplementation, about 6% of people consume less than EAR. The proportion of people with insufficiency is unknown.
Supplementation at 12 to 50 mg daily may support brain health and improve mental performance, according to these studies:
- Thiamine supplementation mood and cognitive functioning. In 1997, this study at 50 mg daily found that Vitamin B1 “was associated with reports of being more clearheaded, composed and energetic ... [and] reaction times were faster following supplementation”.
- Vitamin supplementation for 1 year improves mood. In 1995, this study at ten times RDI found that “in females baseline thiamin status was associated with poor mood and an improvement in thiamin status after 3 months was associated with improved mood”.
For Vitamin B1 in B Complex supplements, the mean dose is 50 mg, which is 4167% RDI, 50% UK UL, and 50% CRN UL. Vitamin B1 is an ingredient in Thrivous Clarity.
Vitamin B2
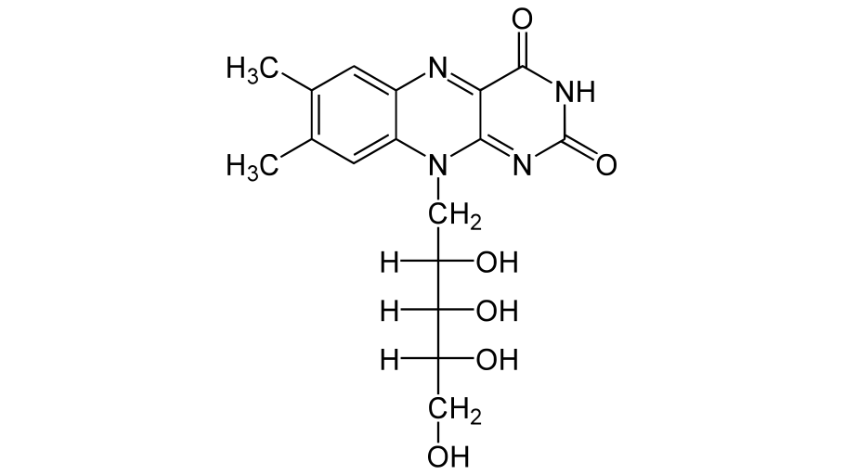
Vitamin B2 vitamers include Riboflavin (Riboflavine), Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide (FAD), Flavin Mononucleotide (FMN or Riboflavin-5-Phosphate). They are found in foods like organ meats, milk, bread products, and fortified cereals.
Regulatory agencies recommend that you consume between 1.3 mg and 1.4 mg daily. In the United States, RDI is 1.3 mg. In the European Union, NRV is 1.4 mg.
Supplements are generally safe up to at least 40 mg daily and perhaps up to 200 mg daily. In the United States and the European Union, UL is not determined. In the United Kingdom, UL is 40 mg.
CRN sets its UL at 200 mg. Regarding the UK UL assessment, CRN notes: "minor and inconsistent adverse effects reported with 400 mg supplemental intake suggest that the [UK] uncertainty factor … is unnecessarily restrictive."
The maximum absorption per dose is at least 27 mg. However, the maximum is probably higher at a diminishing rate. And the bioavailability of different B2 vitamers may be roughly equivalent.
Supplementation may decrease risk of dietary deficiency and insufficiency. In the United States, EAR is 1.1 mg. Before supplementation, about 2% of people consume less than EAR. The proportion of people with insufficiency is unknown.
Supplementation at 25 to 400 mg may provide a notable decrease to migraine. For links to studies, see my list of top tier nootropics.
For Vitamin B2 in B Complex supplements, the mean dose is 50 mg, which is 3846% RDI, 125% UK UL, and 25% CRN UL. Vitamin B2 as Riboflavin-5-Phosphate (FMN) is an ingredient in Thrivous Clarity.
Vitamin B3
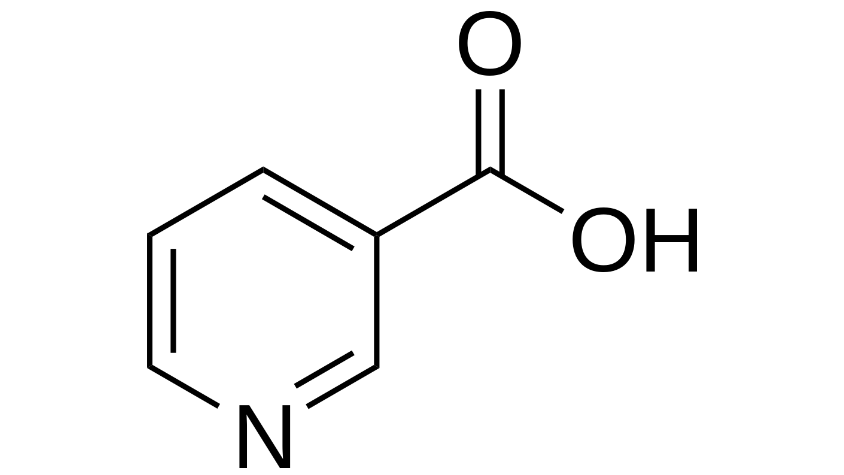
Vitamin B3 vitamers include Nicotinic Acid (Niacin), Nicotinamide (Niacinamide), Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD), Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADP), and Nicotinamide Riboside. They are found in foods like meat, fish, poultry, enriched and whole-grain breads and bread products, and fortified ready-to-eat cereals.
Regulatory agencies recommend that you consume 16 mg daily. In the United States, RDI is 16 mg. In the European Union, NRV is also 16 mg.
Supplements are generally safe up to at least 35 mg daily for the Niacin vitamer and up to 1500 mg daily for the Nicotinamide vitamer. In the United States, UL is 35 mg. In the European Union, UL is 10 mg for Nicotinic Acid and 900 mg for Nicotinamide. In the United Kingdom, UL is 17 mg for Nicotinic Acid and 500 mg for Nicotinamide.
CRN sets its UL at 250 mg for Nicotinic Acid and 1500 mg for Nicotinamide. Regarding the other UL assessments, CRN notes: "flushing reaction in response to supplemental nicotinic acid deserves to be characterized as a nuisance, but not as a hazard." And "CRN UL for excessive supplemental nicotinic acid is based on the hepatotoxic effects at much higher doses, effects that can be clearly hazardous."
Maximum absorption per dose is above the CRN UL. The bioavailability of different B3 vitamers may be roughly equivalent. However, they may function differently in the body.
Supplementation may decrease risk of dietary deficiency and insufficiency. In the United States, EAR is 12 mg. Before supplementation, about 2% of people consume less than EAR; and after supplementation, about 10% consume more than UL. The proportion of people with insufficiency is unknown.
Supplementation may support brain health, according to these studies:
- Dietary niacin and the risk of incident Alzheimer's disease and of cognitive decline. In 2004, this study found that “dietary niacin may protect against AD and age related cognitive decline”.
- Coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide: new therapeutic approach for improving dementia of the Alzheimer type. In 1996, this study found that NADH at 10 mg daily provided "an improvement in [Alzheimer] cognitive dysfunction".
This study had divergent results:
- No evidence for cognitive improvement from oral nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) in dementia. In 2000, this study found that NADH at 10 mg daily "is unlikely to achieve cognitive improvements".
Supplementation above the CRN UL may provide a strong increase to HDL-C and a notable decrease to LDL-C and triglycerides. For links to studies, see my list of top tier geroprotectors.
Supplementation above the CRN UL may provide a subtle decrease to risk of stroke, according to these studies:
- Effect of Niacin Therapy on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease. In 2010, this meta-analysis of seven studies found that “niacin therapy significantly reduced … stroke”.
This study had divergent results:
- Niacin In Patients With Low HDL Cholesterol Levels Receiving Intensive Statin Therapy. In 2011, this study found that “there was no incremental clinical benefit [including no decrease to risk of stroke] from the addition of niacin to statin therapy”.
However, supplementation above the CRN UL may also promote a subtle detrimental effect on blood glucose. For links to studies, see the Vitamin B3 article at Examine.com.
For Vitamin B3 in B Complex supplements, the mean dose is 100 mg, which is 625% RDI, 588% UK UL, and 40% CRN UL. Vitamin B3 as Nicotinamide is an ingredient in Thrivous Clarity.
Vitamin B4
Vitamin B4 may refer to Adenine, Carnitine, or Choline. Consensus science does not currently recognize any of these substances as a vitamin.
However, Carnitine and Choline are both nootropics. Acetyl-L-Carnitine, a form of Carnitine, is in my list of top tier nootropics. Supplementation may provide a notable decrease to ammonia, thereby detoxifying the brain. I consider Alpha-GPC, which contains Choline, to be a second tier nootropic.
Celebrity futurist Ray Kurzweil recommends Acetyl-L-Carnitine and Phosphatidylcholine. Acetyl-L-Carnitine and Alpha-GPC (Choline) are ingredients in Thrivous supplements.
Vitamin B5
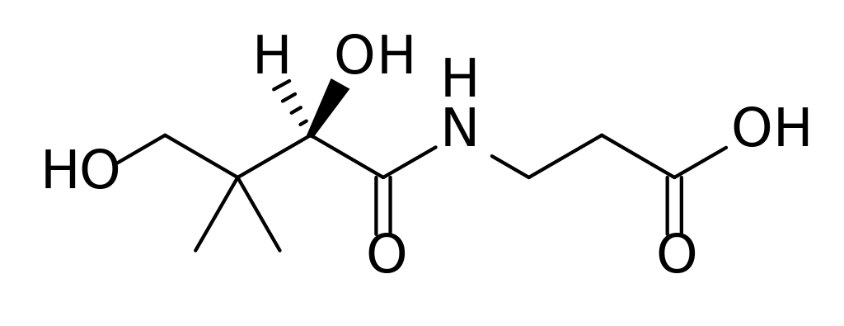
Vitamin B5 vitamers include Coenzyme A, Pantothenate, Pantothenic Acid, Pantothenol, and 4-Phosphopantetheine. It is found in foods like chicken, beef, potatoes, oats, cereals, tomato products, liver, kidney, yeast, egg yolk, broccoli, and whole grains.
Regulatory agencies recommend that you consume between 5 mg and 6 mg daily. In the United States, RDI is 5 mg. In the European Union, NRV is 6 mg.
Supplements are generally safe up to at least 200 mg daily and perhaps up to 1000 mg daily. In the United States and the European Union, UL is not determined. In the United Kingdom, UL is 200 mg.
CRN sets its UL at 1000 mg. Regarding the UK UL assessment, CRN notes: "clinical trial data identified by the [UK] provided evidence that supplemental intakes of 2,000 mg did not produce adverse effects." And "with the absence of adverse effects with daily intakes as high as 10 g, and systemic clinical experience with oral intakes of up to 1,000 mg per day, 1,000 mg per day is selected as the CRN supplemental UL value."
It may not matter much which B5 vitamer you use. The bioavailability of different B5 vitamers may be roughly equivalent.
Supplementation may decrease risk of dietary deficiency and insufficiency. In the United States, EAR is not established. The proportion of people with insufficiency is unknown.
For Vitamin B5 in B Complex supplements, the mean dose is 100 mg, which is 2000% RDI, 50% UK UL, and 10% CRN UL. Vitamin B5 as Calcium Pantothenate is an ingredient in Thrivous Clarity.
Vitamin B6
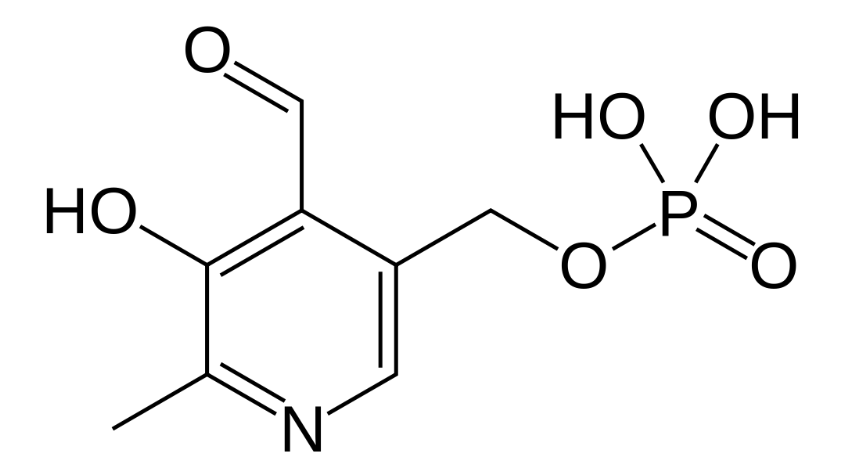
Vitamin B6 vitamers include Pyridoxine (Pyridoxol), Pyridoxine-5-Phosphate, Pyridoxamine, Pyridoxamine-5-Phosphate, Pyridoxal, and Pyridoxal-5-Phosphate. They are found in foods like fortified cereals, organ meats, and fortified soy-based meat substitutes. In the United States, FDA regulates the Pyradoxamine vitamer as a pharmaceutical.
Regulatory agencies recommend that you consume between 1.4 mg and 1.7 mg daily. In the United States, RDI is 1.7 mg. In the European Union, NRV is 1.4 mg.
Supplements are generally safe up to at least 10 mg daily and perhaps up to 100 mg daily. In the United States, UL is 100 mg. In the European Union, UL is 25 mg. In the United Kingdom, UL is 10 mg.
CRN sets its UL at 100 mg. Regarding the other UL assessments, CRN notes: "three government reports based their risk assessment on widely differing datasets and methods, especially in determining uncertainty." It calls attention to "the complete absence of adverse effects in credible, well-designed studies at 100 and 150 mg and only marginal evidence of adverse effects at 200 mg." And it concludes that "100 mg can be confidently identified, with a low level of uncertainty, as a safe level of consumption."
Supplementation may decrease risk of dietary deficiency and insufficiency. In the United States, EAR is 1.1 mg. Before supplementation, about 12% of people consume less than EAR; and after supplementation, about 1% consume more than UL. The proportion of people with insufficiency is unknown.
Supplementation (independent of B Complex consideration) may NOT support brain health or improve mental performance, according to these meta-analyses:
- Effect of Homocysteine Lowering Treatment on Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. In 2012, this meta-analysis found that “supplementation of vitamins B12, B6, and folic acid alone or in combination does not appear to improve cognitive function in individuals with or without existing cognitive impairment”.
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2012 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
- Vitamin B6, B12, and folic acid supplementation and cognitive function: a systematic review of randomized trials. In 2007, this meta-analysis reviewed studies on combinations of B6, B9, and B12. It found that they do "not yet provide adequate evidence of an effect … on cognitive function testing in people with either normal or impaired cognitive function."
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2007 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
- Vitamin B6 for cognition. In 2003, this meta-analysis found “no evidence for short-term benefit from vitamin B6 in improving mood (depression, fatigue and tension symptoms) or cognitive functions”.
This study had divergent results:
- Effects of pyridoxine on dreaming: a preliminary study. In 2002, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study at 250 mg daily found that "Vitamin B-6 may act by increasing cortical arousal during periods of rapid eve movement (REM) sleep".
However, supplementation above the CRN UL may promote risk of nerve damage, according to this and related studies:
- Sensory neuropathy from pyridoxine abuse. A new megavitamin syndrome. In 1983, this study found that “large doses of [Vitamin B6] ... can cause sensory neuropathy or neuronopathy syndromes”.
For Vitamin B6 in B Complex supplements, the mean dose is 50 mg, which is 2941% RDI, 500% UK UL, and 50% CRN UL. Vitamin B6 as Pyridoxal-5-Phosphate is an ingredient in Thrivous Clarity.
Vitamin B7
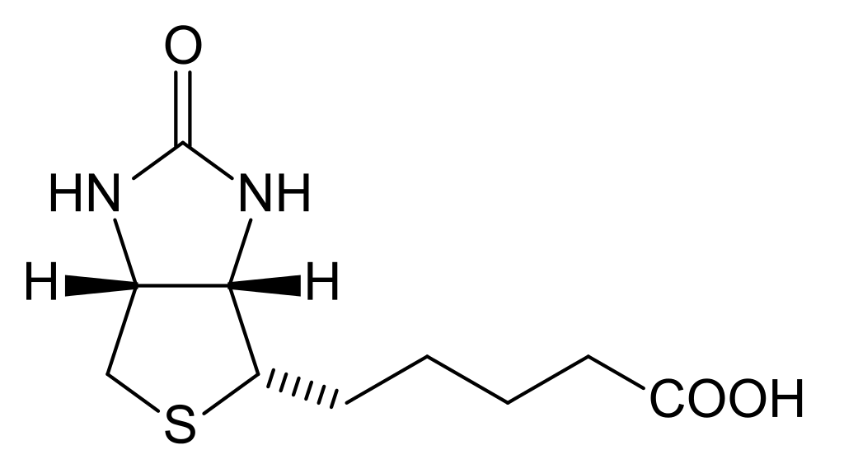
Vitamin B7 vitamers include Biotin. It is found in foods like liver, and smaller amounts in fruits and meats.
Regulatory agencies recommend that you consume between 30 mcg and 50 mcg daily. In the United States, RDI is 30 mcg. In the European Union, NRV is 50 mcg.
Supplements are generally safe up to at least 900 mcg daily and perhaps up to 2500 mcg daily. In the United States and the European Union, UL is not determined. In the United Kingdom, UL is 900 mcg.
CRN sets its UL at 2500 mcg. Regarding the UK UL assessment, CRN notes: "absence of adverse effect at 9mg of biotin per day suggests that biotin supplements with lower amounts are likely to be safe … [and the UK uncertainty factor] is unnecessarily restrictive."
Supplementation may decrease risk of dietary deficiency and insufficiency. In the United States, EAR is not established. The proportion of people with insufficiency is unknown.
For Vitamin B7 in B Complex supplements, the mean dose is 300 mcg, which is 1000% RDI, 33% UK UL, and 12% CRN UL. Vitamin B7 as Biotin is an ingredient in Thrivous Clarity.
Vitamin B8
Vitamin B8 may refer to Adenosine Monophosphate (also known as AMP or Adenylic Acid) or Inositol. Consensus science does not currently recognize either of these substances as a vitamin.
However, Inositol is in my list of top tier nootropics. Supplementation may provide a notable decrease to anxiety and panic attacks.
Vitamin B9
Vitamin B9 vitamers include Folic Acid and Folate. Folate forms include 5-Formyltetrahydrofolate (Folinic Acid) and 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate. 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate forms include D-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate (D-5-MTHF, 6R-D-Methyltetrahydrofolate, or 6R-D-MTHF) and L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate (L-5-MTHF, 6S-L-Methyltetrahydrofolate, or 6S-L-MTHF). They are found in foods like enriched cereal grains, dark leafy vegetables, enriched and whole-grain breads and bread products, and fortified ready-to-eat cereals.
Regulatory agencies recommend that you consume between 200 mcg and 400 mcg daily. In the United States, RDI is 400 mcg. In the European Union, NRV is 200 mcg.
Supplements are generally safe up to at least 1000 mcg daily. In the United States, the European Union, and the United Kingdom, UL is 1000 mcg. CRN also sets its UL at 1000 mcg.
Folate may present a lower risk of adverse effects than Folic Acid. In some cases, 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate may provide greater bioavilability than 5-Formyltetrahydrofolate, particularly for persons with the MTHFR genetic mutation. L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate may have higher antioxidant activity than D-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate.
Supplementation may decrease risk of dietary deficiency and insufficiency. In the United States, EAR is 320 mcg. Before supplementation, about 11% of people consume less than EAR; and after supplementation, about 6% consume more than UL. The proportion of people with insufficiency is unknown.
Supplementation may decrease risk of neural tube birth defects, according to this and related meta-analyses:
- Effects and safety of periconceptional oral folate supplementation for preventing birth defects. In 2015, this meta-analysis found that “Folic acid, alone or in combination with vitamins and minerals, prevents [neural tube defects], but does not have a clear effect on other birth defects”.
Supplementation (independent of B Complex consideration) may NOT support brain health or improve mental performance, according to these meta-analyses:
- Effects of homocysteine lowering with B vitamins on cognitive aging: meta-analysis of 11 trials with cognitive data on 22,000 individuals. In 2014, this meta-analysis found that “homocysteine lowering by using [B9 alone or in combination with B12] vitamins had no significant effect on individual cognitive domains or global cognitive function or on cognitive aging”.
- B-vitamin trials meta-analysis: less than meets the eye. In 2015, this review commented regarding the 2014 meta-analysis that “although the sheer volume of data incorporated into this analysis testifies to the industriousness of its authors, few other conclusions can be drawn”.
- Homocysteine lowering, B vitamins, and cognitive aging. In 2015, this review commented regarding the 2014 meta-analysis that “we are concerned about 3 aspects of this analysis: the choice of trials, the cognitive assessment tools, and the analysis and interpretation of data”.
- Assessing the association between homocysteine and cognition: reflections on Bradford Hill, meta-analyses, and causality. In 2015, this review commented on the 2014 meta-analysis. It claimed that "no conclusion can be made regarding the effects of homocysteine-lowering on cognitive decline, since the trials typically did not include individuals who were experiencing such decline."
- Effect of Homocysteine Lowering Treatment on Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. In 2012, this meta-analysis found that “supplementation of vitamins B12, B6, and folic acid alone or in combination does not appear to improve cognitive function in individuals with or without existing cognitive impairment”.
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2012 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
- B-vitamins and fatty acids in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease and dementia: a systematic review. In 2010, this meta-analysis found “insufficient evidence to draw definitive conclusion on the effect of B vitamins [B9 alone or in combination with other B Vitamins] and fatty acids for the treatment of cognitive decline, dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease”.
- Effect of folic acid, with or without other B vitamins, on cognitive decline: meta-analysis of randomized trials. In 2010, this meta-analysis found “no effect of folic acid, with or without other B vitamins, on cognitive function within 3 years of the start of treatment”.
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2010 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
- Folic acid with or without vitamin B12 for the prevention and treatment of healthy elderly and demented people. In 2008, this meta-analysis found that “the small number of studies which have been done provide no consistent evidence either way that folic acid, with or without vitamin B12, has a beneficial effect on cognitive function of unselected healthy or cognitively impaired older people”.
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2008 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
- Vitamin B6, B12, and folic acid supplementation and cognitive function: a systematic review of randomized trials. In 2007, this meta-analysis reviewed studies on combinations of B6, B9, and B12. It found that they do "not yet provide adequate evidence of an effect … on cognitive function testing in people with either normal or impaired cognitive function."
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2007 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
These studies had divergent results:
- High folate intake is related to better academic achievement in Swedish adolescents. In 2011, this study found that “Folate intake had a positive association with academic achievement in the 15-year-olds”.
- Effect of 3-year folic acid supplementation on cognitive function in older adults in the FACIT trial: a randomised, double blind, controlled trial. In 2007, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that “Folic acid supplementation for 3 years significantly improved domains of cognitive function that tend to decline with age”.
However, supplementation above the UL may promote risk of colon cancer, according to this and related studies:
- Colon cancer in Chile before and after the start of the flour fortification program with folic acid. In 2009, this study found that “a folate fortification program could be associated with an additional risk of colon cancer”.
For Vitamin B9 in B Complex supplements, the mean dose is 400 mcg, which is 100% RDI, 40% UK UL, and 40% CRN UL. Vitamin B9 as L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate is an ingredient in Thrivous Clarity.
Vitamin B10
Vitamin B10 may refer to Para-Aminobenzoic Acid (also known as PABA). Consensus science does not currently recognize this substance as a vitamin.
Vitamin B11
Vitamin B11 may refer to Pteryl-Hepta-Glutamic Acid (also known as PHGA) or Salicylic Acid. Consensus science does not currently recognize either of these substances as a vitamin.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 vitamers include Cyanocobalamin, Adenosylcobalamin, and Methylcobalamin. They are found in foods like fortified cereals, meat, fish, and poultry.
Regulatory agencies recommend that you consume between 2.4 mcg and 2.5 mcg daily. In the United States, RDI is 2.4 mcg. In the European Union, NRV is 2.5 mcg.
Supplements are generally safe up to at least 2000 mcg daily and perhaps up to 3000 mcg daily. In the United States and the European Union, UL is not determined. In the United Kingdom, UL is 2000 mcg. CRN sets its UL at 3000 mcg.
The maximum dose with absorption above a constant 1.2% is between 500 and 1000 mcg.
Cyanocobalamin contains a cyanide molecule. It may be harmless. But Methylcobalamin has become an increasingly popular vitamer. And Methylcobalamin may need to be combined with Adenosylcobalamin to be most broadly effective.
Supplementation may decrease risk of dietary deficiency and insufficiency. In the United States, EAR is 2 mcg. Before supplementation, about 3% of people consume less than EAR. The proportion of people with insufficiency is unknown.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is associated with low red blood cell count and anemia. People on vegan diets have a higher risk because meat is the most common food source of Vitamin B12. However, there are less common food sources that are vegan, such as nutritional yeast. And there are also vegan supplements.
B12 supplements on their own, without the full B Complex, may NOT enhance mental performance. Evidence is summarized in these meta-analyses:
- Effects of vitamin B-12 supplementation on neurologic and cognitive function in older people: a randomized controlled trial. In 2015, this study produced no evidence that "the correction of moderate vitamin B-12 deficiency, in the absence of anemia and of neurologic and cognitive signs or symptoms, has beneficial effects on neurologic or cognitive function in later life."
- Vitamin B12 intake and status and cognitive function in elderly people. In 2013, this meta-analysis found that “current evidence on the relation between vitamin B12 intake or status and cognitive function is not sufficient for consideration in the development of vitamin B12 recommendations”.
- Effect of Homocysteine Lowering Treatment on Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. In 2012, this meta-analysis found that “supplementation of vitamins B12, B6, and folic acid alone or in combination does not appear to improve cognitive function in individuals with or without existing cognitive impairment”.
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2012 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
- Vitamin B6, B12, and folic acid supplementation and cognitive function: a systematic review of randomized trials. In 2007, this meta-analysis reviewed studies on combinations of B6, B9, and B12. It found that they do "not yet provide adequate evidence of an effect … on cognitive function testing in people with either normal or impaired cognitive function."
- The role of B vitamins in preventing and treating cognitive impairment and decline. In 2012, this review commented regarding the 2007 meta-analysis that “ignoring a vast body of observational research in favor of a few RCTs of uneven quality seems imprudent”.
- Vitamin B12 for cognition. In 2003, this meta-analysis found that “evidence of any efficacy of vitamin B12 in improving the cognitive function of people with dementia and low serum B12 levels is insufficient”.
For Vitamin B12 in B Complex supplements, the mean dose is 120 mcg, which is 5000% RDI, 6% UK UL, and 4% CRN UL. Vitamin B12 as Adenosylcobalamin and Methylcobalamin is an ingredient in Thrivous Clarity.
Thrivous Clarity
Based on these and other studies, Thrivous developed Clarity Daily Nootropic. Clarity is an advanced Vitamin B Complex supplement. Each serving of two capsules provides a safe high dose of the most bioavailable B vitamers combined with the most effective natural nootropics. Clarity is designed to support healthy brain function and enhance mental abilities such as memory and focus.
Like all Thrivous supplements, each bottle of Clarity passes through multiple rounds of rigorous quality control. Suppliers test each nutrient to verify its identity, potency, and safety from harmful microbes and metals. Manufacturing tests each nutrient again to double-check the results of our suppliers. And we publish all of our quality test results and certifications on our website for easy reference.
Clarity Daily Nootropic is available in the Thrivous online store. Get yours today!
More Articles
Read more articles at Thrivous, the human enhancement company. You can browse recent articles in Thrivous Views. See other Nootropics or Product Ingredient articles. Or check out an article below.
-
Therapeutic Strategies for Motivation
There is no question that motivation is one of the hardest and yet important factors in life, notes a press ...
-
Sleep Is Essential to Memory and Intelligence
I (and you) have always known that sleep is essential to physical and mental well-being. Now UC San Diego scientists ...



